Developer Guide
- Acknowledgements
- Setting up, getting started
- Design
- Implementation
- Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
- Appendix: Requirements
-
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
- Launch and shutdown
- Adding a multiple choice question (MCQ)
- Adding a true false question (TFQ)
- Adding a short answer question (SAQ)
- Editing a question
- Finding questions
- Deleting a question while all questions are being shown
- Switching Panels and Listing
- Changing Theme
- Quiz
- Quiz specific questions
- Quiz with tags and limits
- Stat
- Adding a note
- Saving data
Acknowledgements
- This project is based on the AddressBook-Level3 project by SE-EDU initiative.
Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
Design
.puml files used to create diagrams in this document can be found in the diagrams folder. Refer to the PlantUML Tutorial at se-edu/guides to learn how to create and edit diagrams.
Architecture
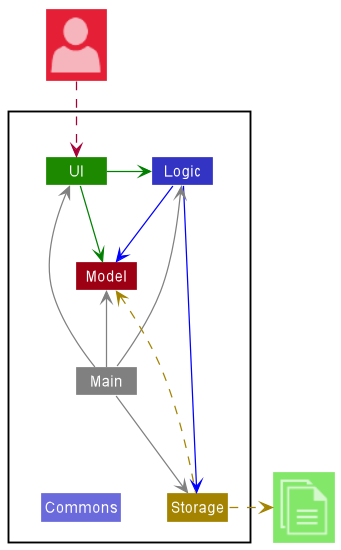
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main components of the architecture
Main has two classes called Main and MainApp. It is responsible for,
- At app launch: Initializes the components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down: Shuts down the components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
The rest of the App consists of four components.
-
UI: The UI of the App. -
Logic: The command executor. -
Model: Holds the data of the App in memory. -
Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command delete question 1.
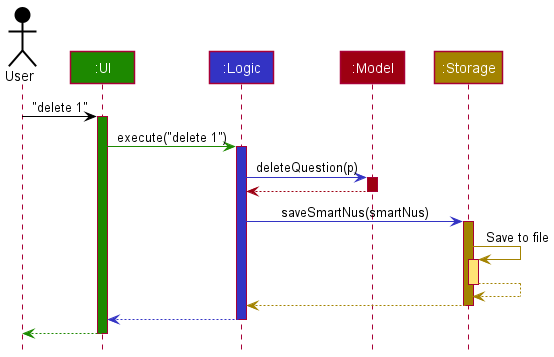
Each of the four main components (also shown in the diagram above),
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - implements its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which follows the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
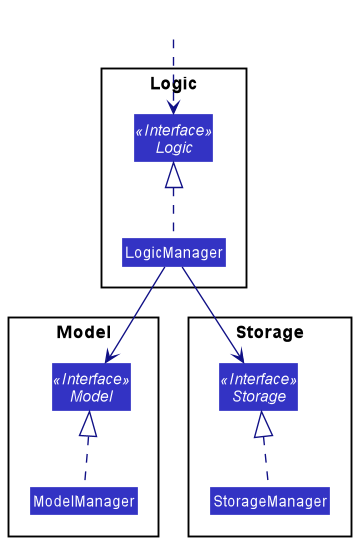
For example, the Logic component defines its API in the Logic.java interface and implements its functionality using the LogicManager.java class which follows the Logic interface. Other components interact with a given component through its interface rather than the concrete class (reason: to prevent outside component’s being coupled to the implementation of a component), as illustrated in the (partial) class diagram below.
The sections below give more details of each component.
UI component
The API of this component is specified in Ui.java
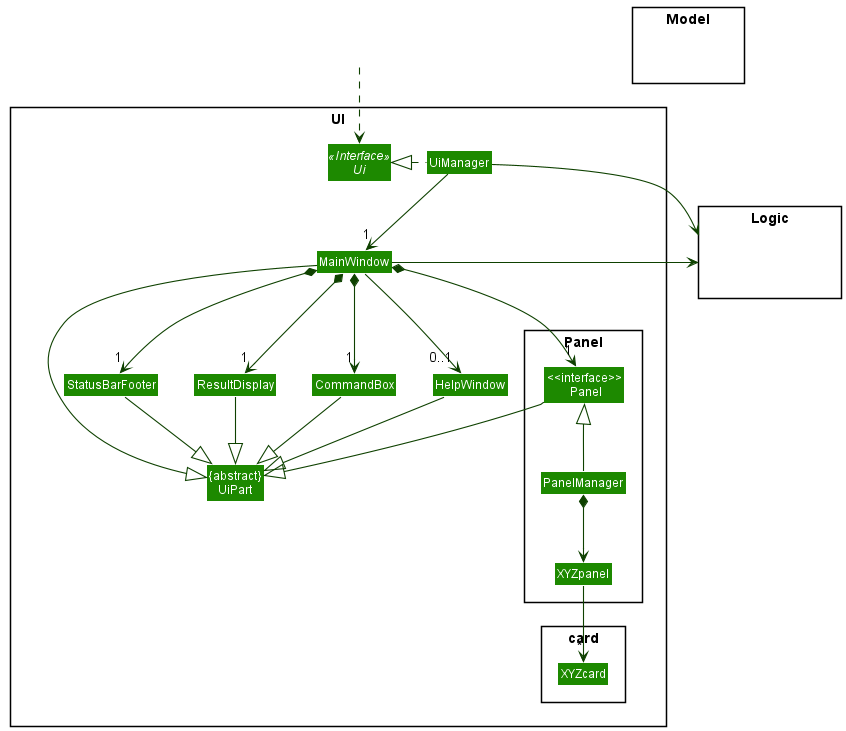
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, Panel, StatusBarFooter etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class which captures the commonalities between classes that represent parts of the visible GUI.
The UI component uses the JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data. - keeps a reference to the
Logiccomponent, because theUIrelies on theLogicto execute commands. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, as it displaysQuestionobject residing in theModel.
Logic component
API : Logic.java
Here’s a (partial) class diagram of the Logic component:
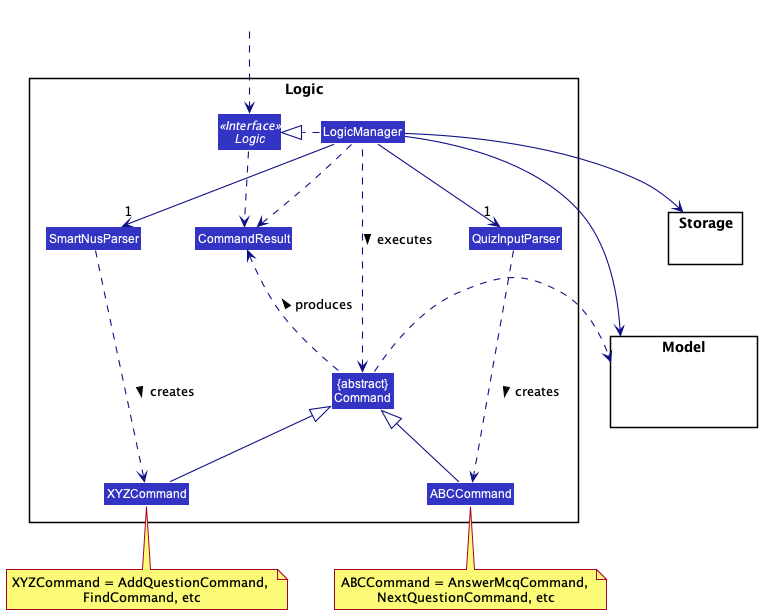
How the Logic component works:
- When
Logicis called upon to execute a command, it uses either theSmartNusParseror theQuizInputParserclass to parse the user command, depending on which window the user is currently on (i.e. Main Window or Quiz Window). - This results in a
Commandobject (more precisely, an object of one of its subclasses,ABCCommandorXYZCommand, which are placeholders for Commands created bySmartNusParserandQuizInputParserrespectively e.g.AddMcqCommandcreated bySmartNusParseris aXYZCommand, whileAnswerMcqCommandcreated byQuizInputParseris aABCCommand) which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command can communicate with the
Modelwhen it is executed (e.g. to add a question forAddMcqCommand). - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is then returned fromLogic.
The Sequence Diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component for the execute("delete question 1") API call.
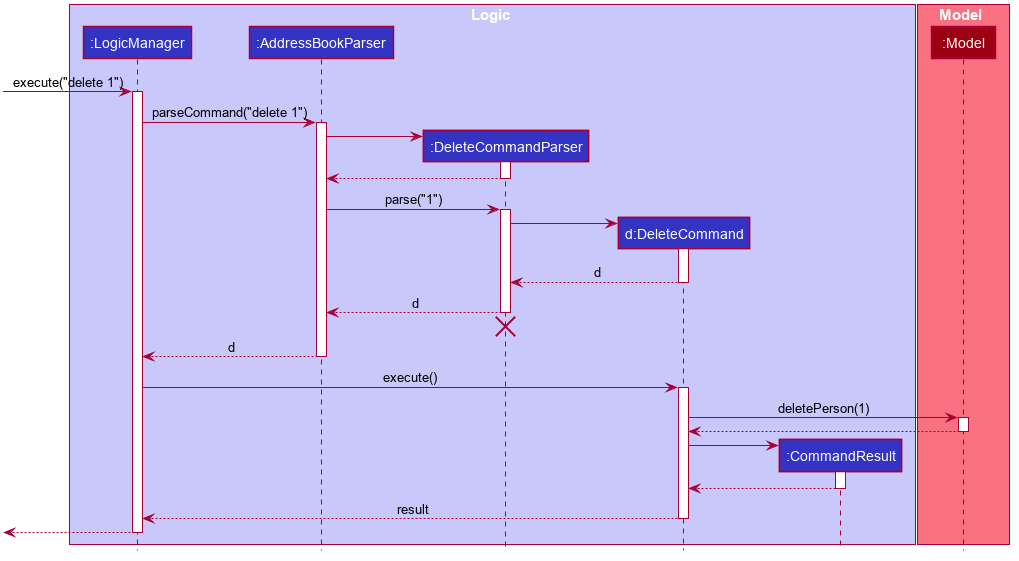
DeleteCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
Here are some other classes in Logic (omitted from the class diagram above) that are used for parsing a user command:
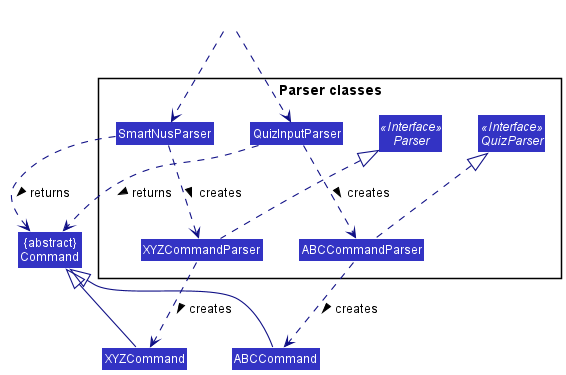
How the parsing works:
- When called upon to parse a user command, the
LogicManagerclass will determine whether theSmartNusParserclass or theQuizInputParserclass will be used to parse the user command. - The selected class it will create
XYZCommandParserorABCCommandParser(XYZandABCare placeholders for the specific command name created bySmartNusParserandQuizInputParserrespectively e.g.,AddMcqCommandParserandAnswerMcqCommandParser) which uses the other classes shown above to parse the user command and create aXYZCommandorABCCommandobject (e.g.,AddMcqCommandorAnswerMcqCommand) which eitherSmartNusParserorQuizInputParserreturns as aCommandobject.- All
XYZCommandParserclasses (e.g.,AddMcqCommandParser,DeleteCommandParser, …) inherit from theParserinterface so that they can be treated similarly where possible e.g, during testing. - All
ABCCommandParserclasses (e.g.,AnswerMcqCommandParser,AnswerTfqCommandParser, …) inherit from theQuizParserinterface so that they can be treated similarly where possible e.g, during testing.
- All
How the Logic component determines which parser to use:
- The
Logiccomponent uses either theSmartNusParseror theQuizInputParserclass to parse the user command, depending on which window the user is currently on (i.e. Main Window or Quiz Window). - Different parsers are used due to different commands being available to the user during the quiz (i.e. the user should not be able to execute
AddMcqCommandwhile in a quiz). - The
LogicManagerclass achieves this through the usage of overloaded methods,parseCommand(String)andparseCommand(String, QuizManager), with the latter for parsing commands while in a quiz. - This was implemented with the consideration that the
QuizInputParserwould require aQuizManagerargument to be passed to variousABCCommandParserandCommandclasses to carry out the necessary various quiz functionality.
Model component
API : Model.java
Here’s a (partial) class diagram of the Model component:
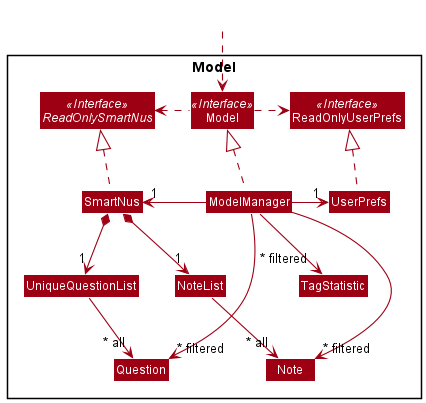
The Model component,
- stores the smartNUS data i.e., all
QuestionandNote(which are contained inUniqueQuestionListandNoteListobjects respectively). - stores the currently ‘selected’
Questionobjects (e.g., results of a search query) as a separate filtered list which is exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<Question>that can be ‘observed’ e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list changes. - stores another list of the currently ‘selected’
Questionobjects for aQuizas a separate filtered list which is also exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<Question>that can be used in the Quiz UI - stores a list of the currently ‘selected’
Noteobjects as a separate filtered list which is also exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<Note>that can be ‘observed’ e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list changes. - stores a list of the currently ‘selected’
TagStatisticobjects as a separate filtered list which is also exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<TagStatistic>that can be ‘observed’ e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list changes. - stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. This is exposed to the outside as aReadOnlyUserPrefobjects. - does not depend on any of the other three components (as the
Modelrepresents data entities of the domain, they should make sense on their own without depending on other components)
Question class
The Question class is an abstract class that stores a Name, Importance, Statistic, Tags and Choices.
A Choice stores a title String, a boolean value isCorrect representing if it is a correct answer to the Question,
and a Set of Strings representing keywords used for evaluating answers to Short Answer Questions.
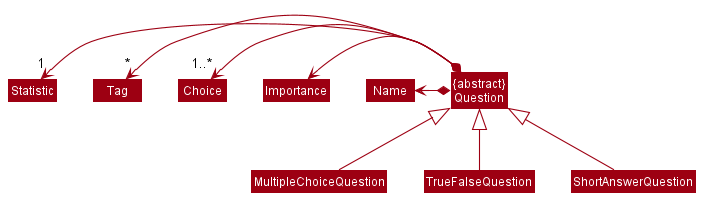
The validity of a Question depends on the type of question.
Types of Questions currently supported by SmartNUS, and their conditions for validity are:
- Multiple Choice Questions
- Has four
Choices in total, exactly one of which is correct
- Has four
- True-False Questions
- Has two
Choices in total, which can only be “True” and “False”, exactly one of which is correct
- Has two
- Short Answer Questions
- Has one
Choicein total which is correct and contains at least onekeyword
- Has one
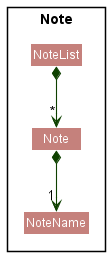
Note class
The Note class is the class that stores a text - defined as a NoteName. The condition for validity of notes is:
- It should not be empty.
The notes are stored in a NoteList that represents a list of notes in which you can add notes, delete notes, or filter notes.
Here is a class diagram of the Notes class.
Statistic Class
The Statistic class is a class that keeps track of the user performance in answering the questions in a quiz.
The performance is tracked by:
- Number of attempts
- Number of correct attempts
performance = number of correct attempts / number of attempts
Here is a sequence diagram of answering a question correctly:
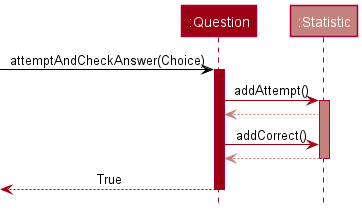
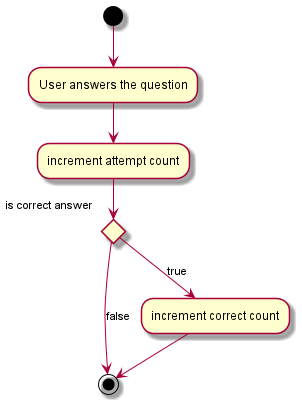
During a quiz, when a user answers a question, the Statistic of the Question is updated.
It will increment the number of attempts by 1 and also increment the number of correct attempts by 1
given that the user answered correctly. If the user does not answer correctly, the number of correct attempts does not increase.
Below is an activity diagram to show the process:
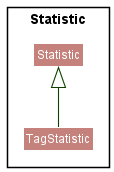
TagStatistic Class
The TagStatistic class inherits from the Statistic class. The TagStatistic class is specifically used to keep track of the statistics of each tags.
Here is the class diagram for Statistic and TagStatistic:
Quiz class
The Quiz class is an interface that is used to manage a quiz. A Quiz can get the current question, go to the next question, go to the previous question, attempt to answer the question, and get the Statistic of the Quiz.
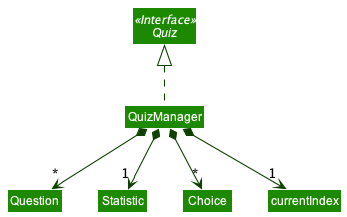
The QuizManager class implements the Quiz interface. It manages the logic behind the quiz, and is created once a quiz is started.
Each QuizManager class stores the following information about the quiz:
-
questions: A list ofQuestionobjects for all the questions in the quiz -
currentIndex: The current question index the user is currently at -
selectedChoices: A list ofChoiceobjects used to keep track of the choices that the user has entered so far -
statistic: AStatisticobject used to keep track of the statistics of the quiz
Storage component
API : Storage.java
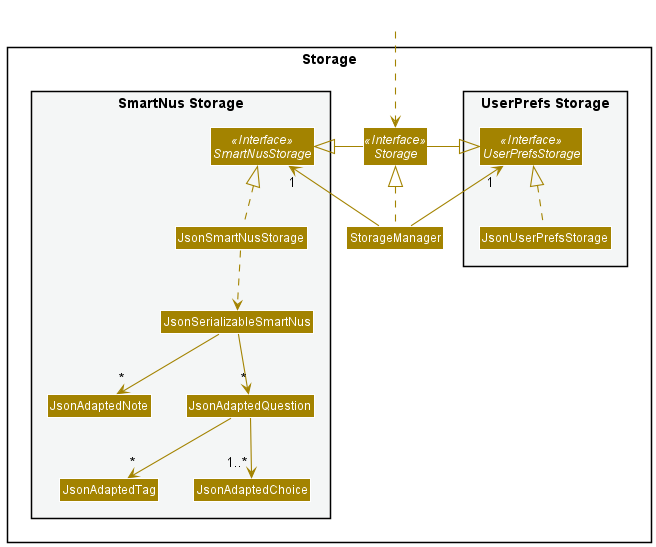
The Storage component,
- can save both SmartNus data and user preference data in json format, and read them back into their corresponding objects. (
QuestionandNoteobjects) - inherits from both
SmartNusStorageandUserPrefStorage, which means it can be treated as either one (if only the functionality of only one is needed). - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent (because theStoragecomponent’s job is to save/retrieve objects that belong to theModel)
Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.smartnus.commons package.
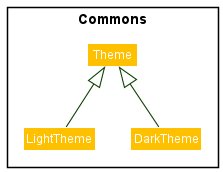
Theme Class
The Theme class is a class that stores the css file of a theme.
Currently, there are two available themes: LightTheme and DarkThemewhich inherits from Theme:
The Theme class is used by the UI component to update the theme and is stored in the Model component as a user preference.
The theme can be changed by executing the ThemeCommand.
Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
Add question feature
Implementation
SmartNus deals with different question types (MCQ, TFQ, SAQ) each of which inherits from the same abstract Question class, as detailed in the Question section.
Adding of questions is done through calling the execute method of the AddQuestionCommand.
The relevant classes, part of the Logic component, are shown in the class diagram below:
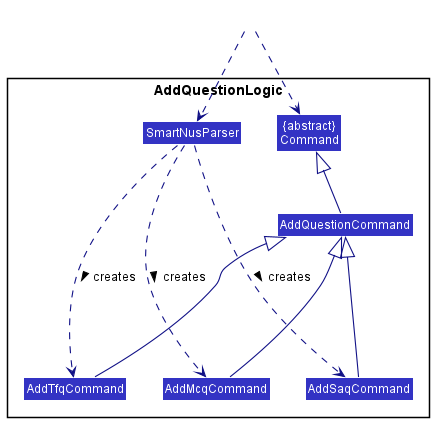
-
AddSaqCommand,AddTfqCommandandAddMcqCommandinherits fromAddQuestionCommand, which inherits from the abstractCommandclass. -
AddQuestionCommandimplements theexecutemethod as required by theCommandabstract class, which adds a question to SmartNus. -
AddSaqCommand,AddTfqCommandandAddMcqCommandall have the sameexecutemethod. (i.e. They do not overrideAddQuestionCommand#execute) -
SmartNusParsercreates the appropriate subtype (AddSaqCommand,AddTfqCommandorAddMcqCommand) ofAddQuestionCommandbased on the user’s input. (e.g. User tells SmartNus to add anmcqquestion,AddMcqCommandis created bySmartNusParser, the same goes for the other question types)
The sequence diagram below illustrates how a tfq is added to SmartNus:
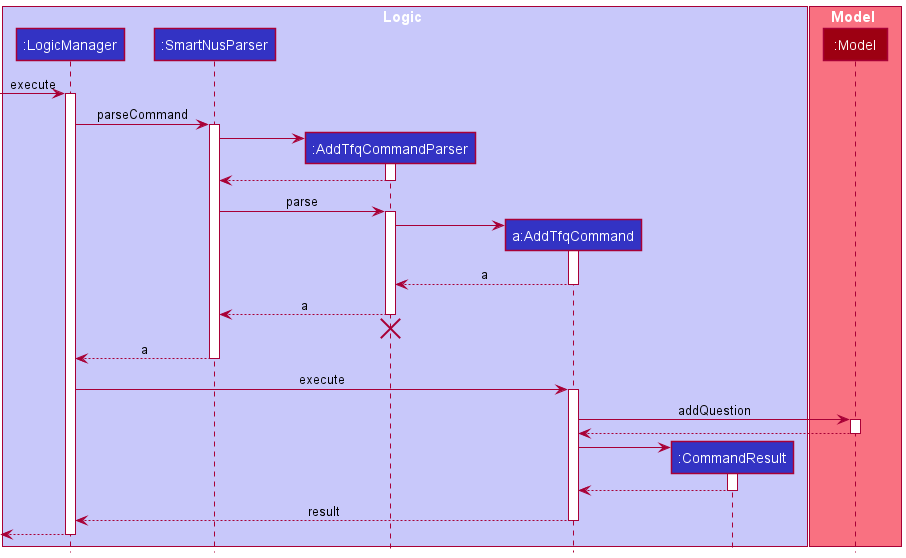
AddTfqCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
Here’s how the tfq is added:
- When
Logicis called upon toexecutethe add tfq command (e.g.tfq qn/ Is 1+1 = 2 ans/T i/1), it uses aSmartNusParserto parse the command via theparseCommandmethod, returning aAddTfqCommandParser. - The
SmartNusParsercalls theparsemethod ofAddTfqCommandParser, which returns aAddTfqCommand. - The
LogicManagercalls theexecutemethod ofAddTfqCommand, which then calls theaddQuestionmethod of the model to add the tfq to SmartNus.
AddMcqCommandParser will be returned by SmartNusParser, which then returns AddMcqCommand upon parsing the user’s input.
Find questions feature
The find questions feature allows users to search for Questions by three parameters: name, tags and importance.
Implementation
The find questions feature is implemented using FindCommandParser, FindCommand and Predicates that implement the Predicate<Question> interface.
Given below is a class diagram of the main classes involved in the implementation of this feature.
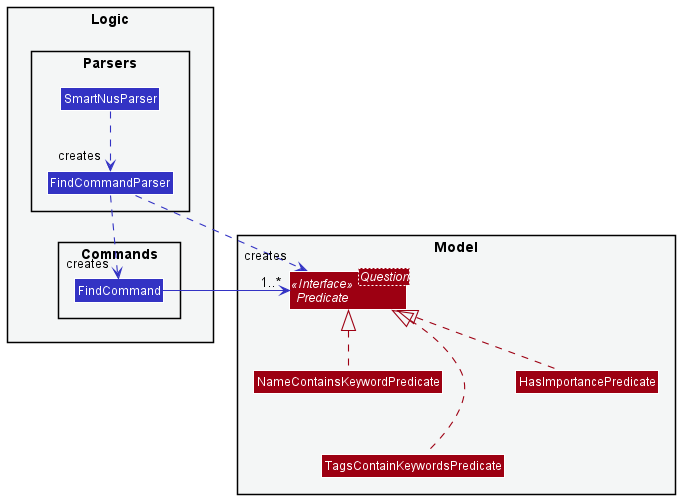
The FindCommandParser parses the user input into predicates that the Questions must match to be included in the FilteredQuestionList.
Each condition is represented by a predicate that extends from Predicate<Question>. The three search parameters in the user input, name, tags and importance,
are parsed and used to create the NameContainsKeywordsPredicate, TagsContainKeywordsPredicate and HasImportancePredicate respectively.
| Predicate | Function |
|---|---|
NameContainsKeywordsPredicate |
Checks if a Question’s Name contains all the given keywords |
TagsContainKeywordsPredicate |
Checks if a Question contains at least one Tags whose name matches a keywords |
HasImportancePredicate |
Checks if a Question has a particular Importance value |
These predicates are passed from the FindCommandParser to the FindCommand.
FindCommand composes these predicates into a logical AND of all predicates. When the FindCommand is executed,
it updates the FilteredQuestionList with Questions that match this composed predicate, and hence satisfy all the
user’s search conditions. Given below is a sequence diagram that shows the execution of a FindCommand when a user
executes find t/CS2103T.
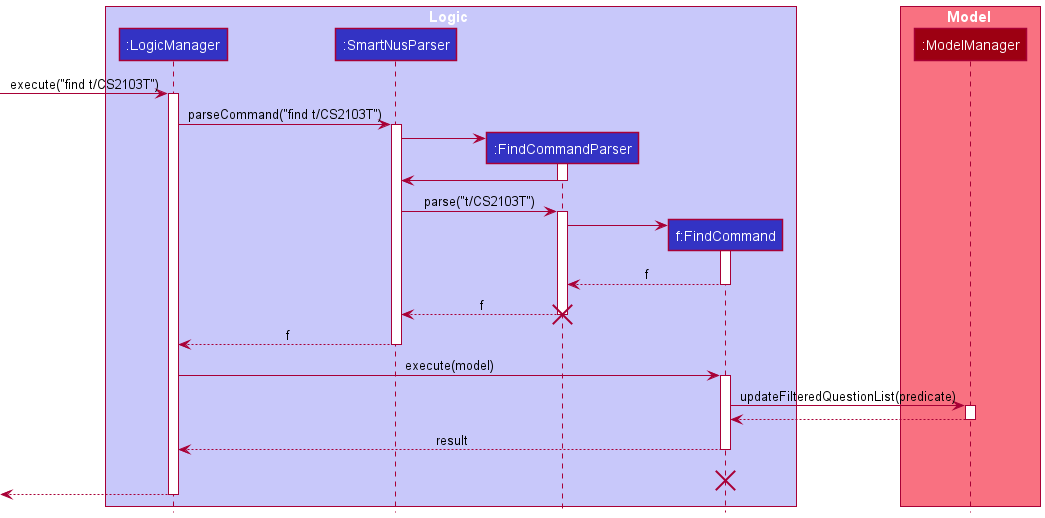
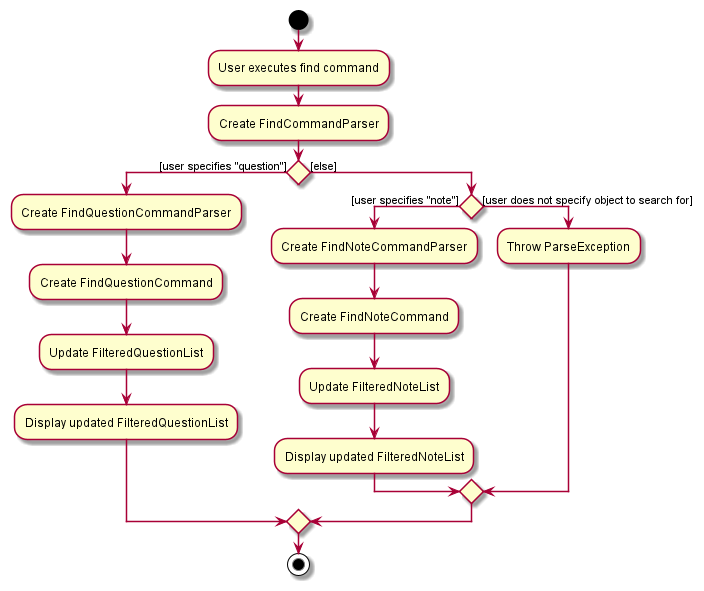
Proposed Extensions
The find feature currently only supports finding questions. It can be extended to search for both Questions and Notes.
Here is the proposed implementation of such a feature:
- The
FindCommandParserwill take in an additional parameter, either “note” or “question”. - Depending on which item the user wants to search for, the
FindCommandParserwill create aFindNoteParseror aFindQuestionParser. - The parsers will parse user inputs into either
Predicate<Note>orPredicate<Question>, depending on the item that the user is searching for. - If the user is searching for
Notes, aFindNoteCommandwill be generated. If the user is searching forQuestions, aFindQuestionCommandis created. The activity diagram below illustrates this implementation.
Change Theme Feature
The Theme class is used by the UI component to update the theme and is stored in the Model component as a user preference.
The theme can be changed by executing the ThemeCommand.
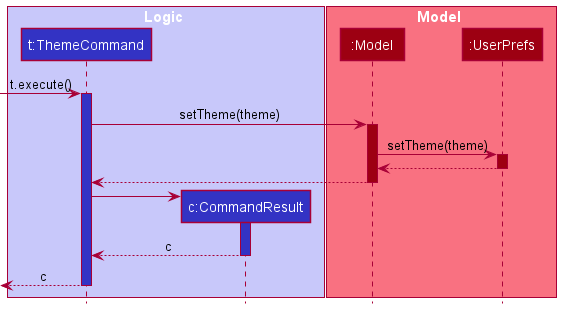
Here is a sequence diagram when the ThemeCommand is executed with a given Theme object called theme inside the ThemeCommand. Currently the theme object can either be a LightTheme or DarkTheme
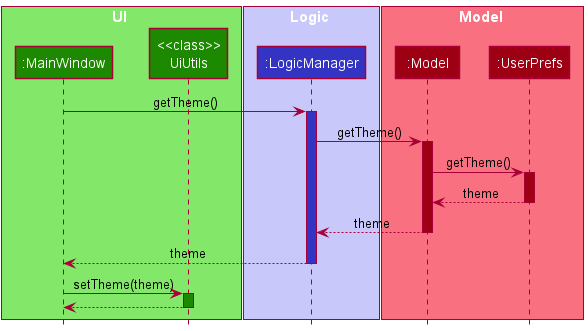
Once a Theme is kept inside the Model, the UI component can fetch the Theme and render it accordingly:
The reason why a Theme is kept inside the Model’s UserPrefs is because it allows the current theme to be saved in the storage as a user preference.
Without saving it in the storage, the user will have to keep changing the theme every time the user opens the app.
Quiz feature
All features related to the quiz functionality.
Starting a quiz
The start quiz feature allows users to start a quiz from the main window.
Implementation
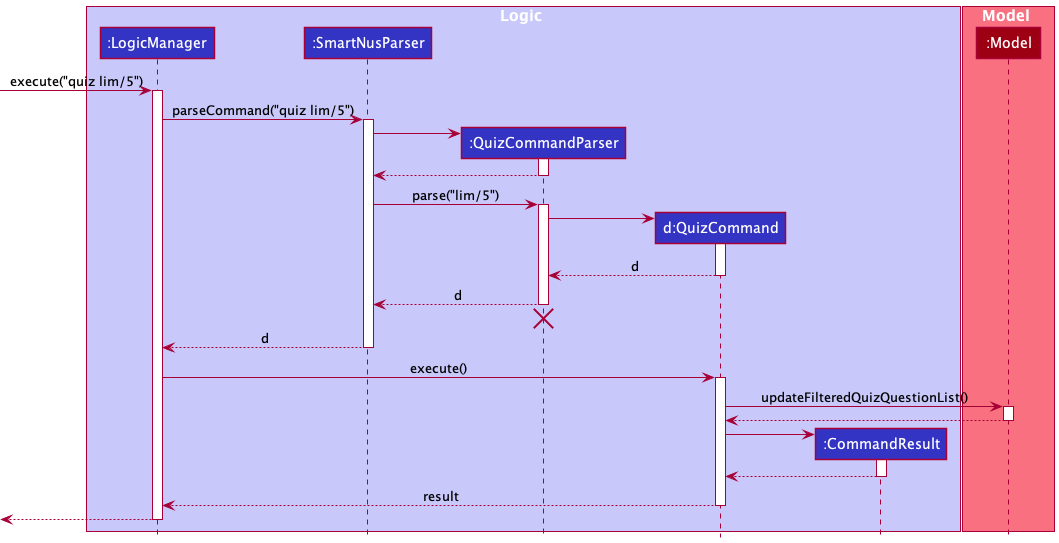
The quiz feature is facilitated by MainWindow, LogicManager, SmartNusParser and QuizCommand. Given below is an example usage scenario of how the start quiz mechanism behaves at each step.
- User input
quiz lim/5fromMainWindowclass in the Ui component is passed to theLogicManager#execute()method. -
LogicManagerwill then callSmartNusParser#parserCommand(), which will create aQuizCommandParser. - Additionally,
SmartNusParserwill then call theQuizCommandParser#parse()method to parse the argumentslim/5, which will create aQuizCommand. -
QuizCommand#execute()will be invoked byLogicManagerto execute the command, which will then callModel#updateFilteredQuizQuestionList()to update the questions in theModel. - The
CommandResultis then returned back toMainWindowwhich will then create a newQuizWindowto be displayed.
Below is the sequence diagram to show how the quiz is started.
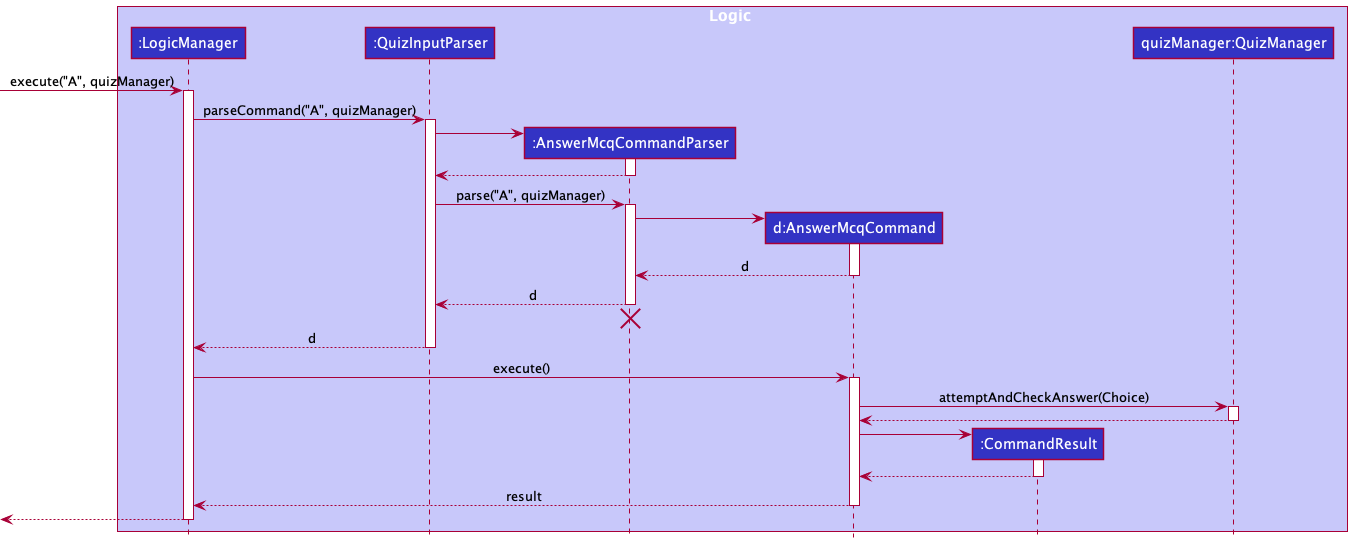
Answering of questions
The answering of questions feature allows users to select their desired choice for questions during a quiz.
Implementation
Given below is an example usage scenario of how the mechanism of answering a multiple choice question behaves at each step.
- User input
Aand theQuizManagerobject from theQuizWindowclass in the Ui component are passed to theLogicManager#execute()method. -
LogicManagerwill then callQuizInputParser#parserCommand(), which will create aAnswerMcqCommandParser. - Additionally,
QuizInputParserwill then call theAnswerMcqCommandParser#parse()method to parse the argumentsAand theQuizManagerobject, which will create aAnswerMcqCommand. -
AnswerMcqCommand#execute()will be invoked byLogicManagerto execute the command, which will then callQuizManager#answerAndCheckAnswer()to update choices inQuizManager. - The
CommandResultis then returned back toQuizWindowwhich will update the Ui with the updated message and the selected choice.
Below is the sequence diagram to show how a multiple choice question is answered.
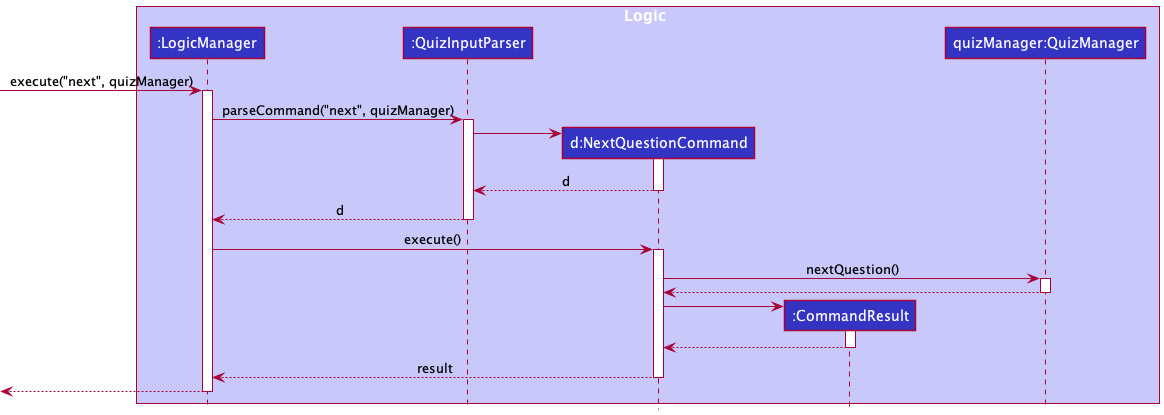
Next question
The next question feature allows users to proceed to the next question during a quiz.
Implementation
Given below is an example usage scenario of how the mechanism of proceeding to the next question behaves at each step.
- User input
nextand theQuizManagerobject from theQuizWindowclass in the Ui component are passed to theLogicManager#execute()method. -
LogicManagerwill then callQuizInputParser#parserCommand(), which will create aNextQuestionCommand. -
NextQuestionCommand#execute()will be invoked byLogicManagerto execute the command, which will then callQuizManager#nextQuestion()to update the current question index inQuizManager. - The
CommandResultis then returned back toQuizWindowwhich will update the Ui with the updated message and question.
Below is the sequence diagram to show how the next question is shown.
[Proposed] Undo/redo feature
Proposed Implementation
The proposed undo/redo mechanism is facilitated by VersionedSmartNus. It extends SmartNus with an undo/redo history, stored internally as an smartNusStateList and currentStatePointer. Additionally, it implements the following operations:
-
VersionedSmartNus#commit()— Saves the current smartNus state in its history. -
VersionedSmartNus#undo()— Restores the previous smartNus state from its history. -
VersionedSmartNus#redo()— Restores a previously undone smartNus state from its history.
These operations are exposed in the Model interface as Model#commitSmartNus(), Model#undoSmartNus() and Model#redoSmartNus() respectively.
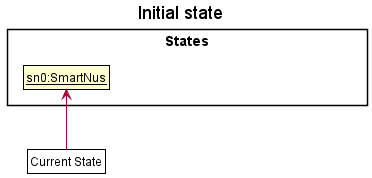
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the undo/redo mechanism behaves at each step.
Step 1. The user launches the application for the first time. The VersionedSmartNus will be initialized with the initial smartNus state, and the currentStatePointer pointing to that single smartNus state.
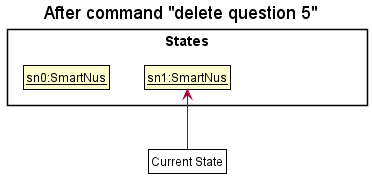
Step 2. The user executes delete 5 command to delete the 5th question in the smartNus. The delete command calls Model#commitSmartNus(), causing the modified state of the smartNus after the delete 5 command executes to be saved in the SmartNusStateList, and the currentStatePointer is shifted to the newly inserted smartNus state.
Step 3. The user executes add n/David … to add a new question. The add command also calls Model#commitSmartNus(), causing another modified smartNus state to be saved into the smartNusStateList.
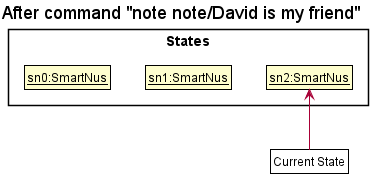
Model#commitSmartNus(), so the smartNus state will not be saved into the smartNusStateList.
Step 4. The user now decides that adding the question was a mistake, and decides to undo that action by executing the undo command. The undo command will call Model#undoSmartNus(), which will shift the currentStatePointer once to the left, pointing it to the previous smartNus state, and restores the smartNus to that state.
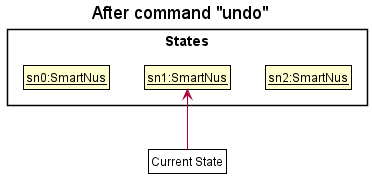
currentStatePointer is at index 0, pointing to the initial SmartNus state, then there are no previous SmartNus states to restore. The undo command uses Model#canUndoSmartNus() to check if this is the case. If so, it will return an error to the user rather
than attempting to perform the undo.
The following sequence diagram shows how the undo operation works:
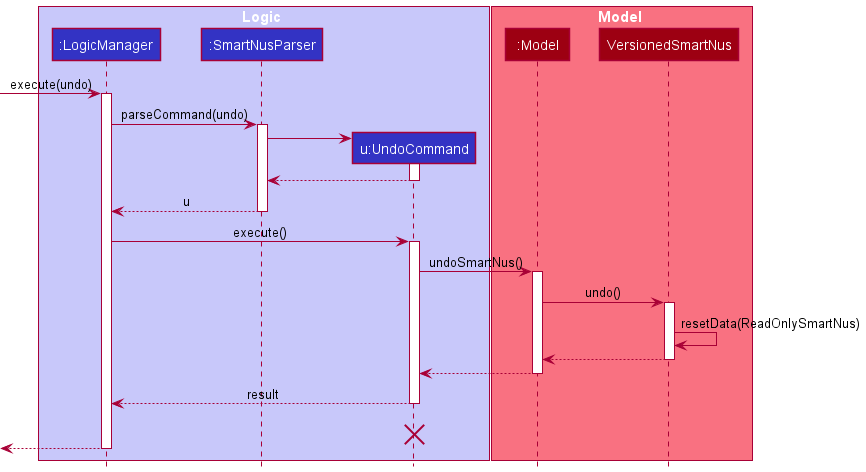
UndoCommand should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
The redo command does the opposite — it calls Model#redoSmartNus(), which shifts the currentStatePointer once to the right, pointing to the previously undone state, and restores the smartNus to that state.
currentStatePointer is at index smartNusStateList.size() - 1, pointing to the latest smartNus state, then there are no undone SmartNus states to restore. The redo command uses Model#canRedoSmartNus() to check if this is the case. If so, it will return an error to the user rather than attempting to perform the redo.
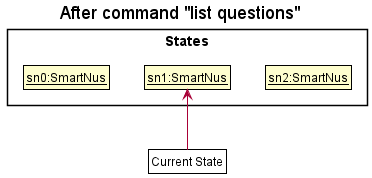
Step 5. The user then decides to execute the command list. Commands that do not modify the smartNus, such as list, will usually not call Model#commitSmartNus(), Model#undoSmartNus() or Model#redoSmartNus(). Thus, the smartNusStateList remains unchanged.
Step 6. The user executes clear, which calls Model#commitSmartNus(). Since the currentStatePointer is not pointing at the end of the smartNusStateList, all smartNus states after the currentStatePointer will be purged. Reason: It no longer makes sense to redo the add n/David … command. This is the behavior that most modern desktop applications follow.
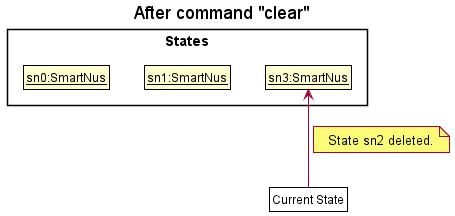
The following activity diagram summarizes what happens when a user executes a new command:
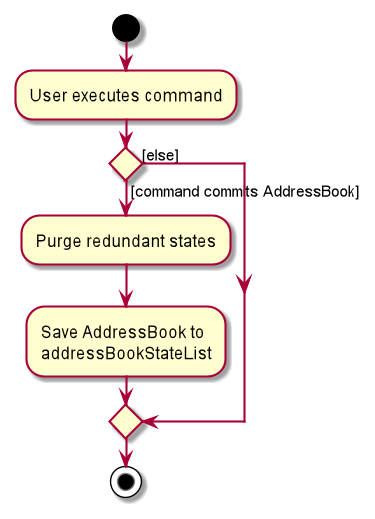
Design considerations:
Aspect: How undo & redo executes:
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Saves the entire smartNus.
- Pros: Easy to implement.
- Cons: May have performance issues in terms of memory usage.
-
Alternative 2: Individual command knows how to undo/redo by
itself.
- Pros: Will use less memory (e.g. for
delete, just save the question being deleted). - Cons: We must ensure that the implementation of each individual command are correct.
- Pros: Will use less memory (e.g. for
{more aspects and alternatives to be added}
[Proposed] Data archiving
{Explain here how the data archiving feature will be implemented}
Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile:
- needs to organise and revise materials for many modules
- wants to note down important information in the form of questions and answers that they can quiz themselves on
- prefer desktop apps over other types
- can type fast
- prefers typing to mouse interactions
- is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value proposition: organise and revise information faster than a typical mouse/GUI driven app
User stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that I can… |
|---|---|---|---|
* * * |
NUS Student | add a multiple choice question to the topic | review the question in MCQ style |
* * * |
NUS Student | add an answer to the multiple choice question | see the correct answer during the review |
* * * |
NUS Student | add a note to remember things about mods | remember points about modules |
* * * |
NUS Student | delete the question and at the same time delete all answers belonging to that question | remove questions and answer that are not needed |
* * * |
NUS Student | do a quiz containing only questions from a certain tag | revise questions for the specific tag |
* * * |
NUS Student | specify the number of questions to be included in any quiz | revise the number of questions taking into account time constraints or the importance I place on that module/topic, rather than having to go through all questions |
* * * |
NUS Student | see the list of all commands | know what commands to use to perform a specific task that I want |
* * * |
NUS Student | specify the number of questions to be included in any quiz | revise the number of questions taking into account time constraints or the importance I place on that module/topic, rather than having to go through all questions |
* * * |
NUS Student | add tags | tag questions to categorise them and search through them easily |
* * * |
NUS Student | delete existing tag | delete unneeded tags |
* * * |
NUS Student | add a True or False question to the topic | review the question in T/F style |
* * * |
NUS Student | add an open ended question to the topic | review the question open endedly |
* * * |
NUS Student | add an answer to the True or False question | see the correct answer during the review |
* * * |
NUS Student | add an answer to the open ended question | see the correct answer during the review |
* * * |
NUS Student | tag questions with custom tags (e.g. midterm, quiz, finals) | mark questions (add a note) |
* * |
NUS Student | end the quiz mid way | end the quiz without finishing it, and return to question list |
* * |
NUS Student | search questions by tag | filter out questions based on the specific tags |
* * |
NUS Student | search questions by keyword | filter out questions based on the specific keyword |
* * |
NUS Student | update existing tag | change a tag if there is a typo |
* * |
NUS Student | edit the multiple choice question | amend the question just in case I made a mistake |
* * |
NUS Student | edit the True or False question | amend the question just in case I made a mistake |
* * |
NUS Student | edit the open ended question | amend the question just in case I made a mistake |
* * |
NUS Student | edit the multiple choice answer | amend the answer just in case I made a mistake |
* * |
NUS Student | edit the True or False answer | amend the answer just in case I made a mistake |
* * |
NUS Student | edit the open ended answer | amend the answer just in case I made a mistake |
* * |
NUS Student | mark a review as correct | track which questions I answered correctly |
* * |
NUS Student | mark a review as incorrect | track which questions I need to review again |
* |
NUS Student | undo a command | undo something that I did carelessly |
* |
NUS Student | add an exam date to a tag | prioritize which modules to study for |
* |
NUS Student | view how many times I have answered any question correctly and incorrectly | identify areas of improvement to focus on during revision |
* |
NUS Student | view how many times I have answered questions from a particular topic correctly and incorrectly | identify areas of improvement to focus on during revision |
* |
NUS Student | have Demo data already in the application [modules, QnA, tags] | see how the application works and try it out easily |
* |
NUS Student | create a deadline (date) for the selected topic | manage my time to review topics |
* |
NUS Student | view deleted questions | still see the questions I might need but have deleted |
* |
NUS Student | restore deleted questions | to restore questions that I deleted but need again |
* |
NUS Student | delete everything and start fresh | get rid of all data I have entered so far |
* |
NUS Student | go back or forward in the question list | review again the questions I have answered |
Use cases
(For all use cases below, the System is the SmartNUS and the Actor is the user, unless specified otherwise)
Use case: List questions
MSS
- User requests to list questions.
- SmartNUS displays a list of all stored questions.
Extensions
- 1a. User does not specify the keyword
question. -
SmartNUS shows error message.
Use case ends.
Use case: List notes
MSS
- User requests to list notes.
- SmartNUS displays a list of all stored notes.
Extensions
- 1a. User does not specify the keyword
note. -
SmartNUS shows error message.
Use case ends.
Use case: List tag
MSS
- User requests to list tag.
- SmartNUS displays a list of all stored tags.
Extensions
- 1a. User does not specify the keyword
tag. -
SmartNUS shows error message.
Use case ends.
Use case: Add Multiple Choice question and options
MSS
- User requests to add an MCQ question and its options, indicating the correct answer.
- SmartNUS saves the question, its options and the correct answer.
Extensions
- 1a. User does not specify any options.
-
SmartNUS shows error message.
Use case ends.
-
- 1b. User does not specify the correct answer.
-
SmartNUS shows error message.
Use case ends.
-
- 1c. User specifies more than 3 incorrect options.
-
SmartNUS shows error message.
Use case ends.
-
Use case: Add True/False question
MSS
- User requests to add a True/False question, indicating the correct answer.
- SmartNUS saves the question and the correct answer.
Extensions
- 1a. User does not specify the correct answer.
-
1a1. SmartNUS shows error message.
Use case ends.
-
- 1b. User specifies a blank answer.
-
1b1. SmartNUS shows error message.
Use case ends.
-
Use case: Add Short Answer question
MSS
- User requests to add a Short Answer question, indicating the correct answer and keywords.
- SmartNUS saves the question, the correct answer and keywords.
Extensions
- 1a. User does not specify the correct answer.
- SmartNUS shows error message.
Use case ends.
- 1b. User specifies an answer without keywords.
- SmartNUS shows error message.
Use case ends.
Use case: Delete a question
MSS
- User requests to list questions.
- SmartNUS shows a list of all questions.
- User requests to delete a specific question in the list.
-
SmartNUS deletes the question.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 2a. The list is empty.
-
2a1. SmartNUS shows message that there are no questions.
Use case ends.
-
- 3a. The given index is invalid.
-
3a1. SmartNUS shows an error message.
Use case resumes at Step 2.
-
Use case: Delete a note
MSS
- User requests to list notes.
- SmartNUS shows a list of all notes.
- User requests to delete a specific note in the list.
-
SmartNUS deletes the note.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 2a. The list is empty.
-
2a1. SmartNUS shows message that there are no notes.
Use case ends.
-
- 3a. The given index is invalid.
-
3a1. SmartNUS shows an error message.
Use case resumes at Step 2.
-
Use case: Find questions
MSS
- User requests to list questions containing specific keywords, tags and/or importance.
- SmartNUS shows a list of questions that contain all the keywords, at least one of the tags and the importance value (if these parameters are specified).
Extensions
- 1a. User does not specify any parameters (keywords, tags and importance).
- 1a1. SmartNUS shows an error message.
Use case ends.
- 1b. User specifies tag names that are not alphanumeric.
- 1b1. SmartNUS shows an error message.
Use case ends.
- 1c. User specifies an invalid importance value.
- 1c1. SmartNUS shows an error message.
Use case ends.
- 2a. There are no questions in SmartNUS that satisfy the user’s search conditions.
-
2a1. SmartNUS shows message that there are no questions.
Use case ends.
-
Use case: Edit a question
MSS
- User requests to list questions.
- SmartNUS shows a list of all questions.
- User requests to edit a specific question in the list with new values.
-
SmartNUS updates the question’s details to those specified by the user.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 2a. The list is empty.
-
2a1. SmartNUS shows message that there are no questions.
Use case ends.
-
- 3a. The given index is invalid.
-
3a1. SmartNUS shows an error message.
Use case resumes at Step 2.
-
- 3b. The values provided by the user to update the question are invalid.
-
3b1. SmartNUS shows an error message.
Use case resumes at Step 2.
-
Use case: Start a quiz
MSS
- User requests to start a quiz, specifying number of questions and tags.
- SmartNUS shows a question from one of the specified tags and its options.
- User chooses one option.
- SmartNUS shows the correct option (answer).
- Steps 2 to 4 are repeated until the user has answered the number of questions he/she specified when starting the quiz.
- SmartNUS shows the user’s score (number of questions correct and total number of questions answered).
Extensions
- 1a. Number of questions is invalid (negative or more than total number of questions).
-
1a1. SmartNUS shows error message.
Use case ends.
-
- 1b. At least one tag does not exist.
-
1b1. SmartNUS shows an error message.
Use case ends.
-
- 2a. User did not specify any tags.
-
2a1. SmartNUS shows any question (that has not yet been shown in the quiz) and its options.
Use case resumes at Step 3.
-
- 5a. User did not specify number of questions.
-
5a1. Steps 2 to 4 are repeated until all questions from the specified tags have been shown.
Use case resumes at Step 6.
-
Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
11or above installed. - Should be able to hold up to 500 questions and 500 notes without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage.
- A student with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
- The data should be stored locally and should be in an editable json file.
- The product should be for a single user at a time.
- The final product should be a result of morphing the given AB3 code base.
- The final product should be self-contained i.e should not prompt the user to open any links.
- The final product should be fully functional without the internet.
Glossary
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS-X
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Launch and shutdown
-
Initial launch
-
Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
-
Double-click the jar file Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample contacts. The window size may not be optimum.
-
Saving window preferences
-
Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
-
Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file.
-
Adding a multiple choice question (MCQ)
-
Prerequisites: List all questions using the
list questioncommand. Multiple questions in the list. -
Test case:
mcq qn/What is 5+2? ans/7 opt/1 opt/2 opt/3 i/2 t/Math
Expected: An mcqWhat is 5+2?with options1, 2, 3and answer7with importance2and tagMathis created. -
Test case:
mcq qn/What is 5+3? ans/8 opt/2 opt/2 opt/3 i/2 t/Math
Expected: Question is not created as options are duplicates -
Other incorrect mcq commands to try:
mcq,mcq ans/3,...Expected: Question is not created as there are missing compulsory parameters.
Adding a true false question (TFQ)
-
Prerequisites: List all questions using the
list questioncommand. Multiple questions in the list. -
Test case:
tfq qn/Is 5+2 = 8? ans/f i/2 t/Math
Expected: An tfqWhat is 5+2?with answerfalse,importance2and tagMathis created. -
Test case:
tfq qn/Is 5+2 = 8? ans/yes i/2 t/Math
Expected: Question is not created as answer needs to be eitherTorF -
Other incorrect mcq commands to try:
tfq,tfq qn/Is 5+2 = 8?,...Expected: Question is not created as there are missing compulsory parameters.
Adding a short answer question (SAQ)
-
Prerequisites: On the Question panel/viewing questions (e.g. after running the
list questionorfindcommands). -
Test case:
saq qn/What is the name of this app? ans/k/SmartNUS i/3Expected: A new short answer question with the specified details is added and shown on the displayed list of questions.
-
Test case:
saq qn/What is the name of this app? ans/SmartNUS i/3Expected: No new question is added and an error message is thrown as the answer must contain at least one keyword (specified by
k/). -
Test case:
saq qn/What is the name of this app? ans/k/SmartNUSExpected: No new question is added and an error message is thrown as the user failed to specify the importance (
i/) of the question.
Editing a question
-
Prerequisites: On the Question panel/viewing questions (e.g. after running the
list questionorfindcommands). List displayed contains at least 3 questions. The first one is a Multiple Choice Question, the second is a True False Question and the third is a Short Answer Question. -
Test case:
edit 1 qn/This is my new question ans/1 opt/2 opt/3 opt/4 t/Expected: First question in the list is edited with the new title, new answer and options, and all tags (if the question had any) are removed.
-
Test case:
edit 2 ans/T t/JavaExpected: Second question in the list is updated with the new answer (True) and now has one tag titled Java
-
Test case:
edit 3 ans/k/mitochondria i/3Expected: Third question in the list is updated with a new answer, keyword and importance.
-
Test case:
edit 1Expected: No question is edited. Error message is shown as no parameters to be edited are specified.
-
Test case:
edit 1 qn/Expected: No question is edited. Error mesesage is shown as
qn/parameter cannot be empty.
Finding questions
-
Prerequisites: On the Question panel/viewing questions (e.g. after running the
list questionorfindcommands). -
Test case:
find t/Java t/CS2103TExpected: All questions in SmartNUS tagged with Java, CS2103T or both are shown.
-
Test case:
find coding standard t/cs2103t i/2Expected: All questions that contain the full words “coding” and “standard” in their titles (in any order) AND are tagged with “cs2103t” AND have importance of 2 are shown.
-
Test case:
findExpected: An error message is shown as user did not specify any parameters to find by.
Deleting a question while all questions are being shown
-
Prerequisites: List all questions using the
list questioncommand. Multiple questions in the list. -
Test case:
delete question 1
Expected: First question is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted question shown in the status message. Timestamp in the status bar is updated. -
Test case:
delete question 0
Expected: No question is deleted. Error details shown in the status message. Status bar remains the same. -
Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete,delete note x,...(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
Switching Panels and Listing
- Switch panel to view all questions
- Test case:
list question
Expected: A list of questions shown. The status bar at the bottom saysQuestionsand the UI looks like this: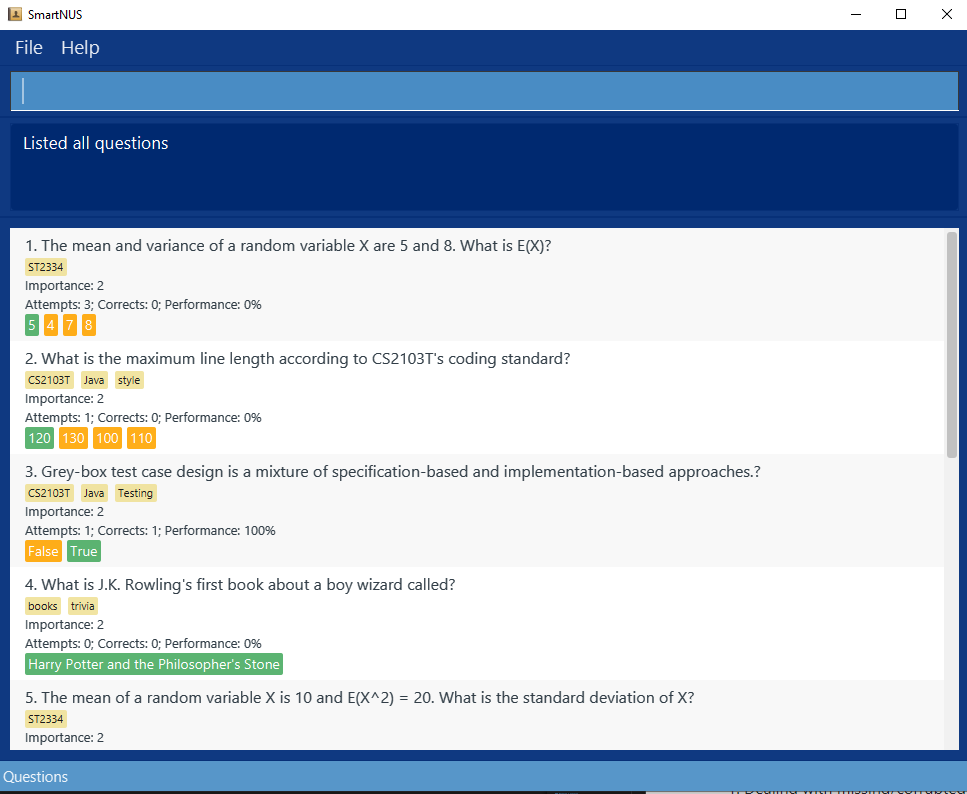
- Test case:
- Switch panel to view all notes
- Test case:
list note
Expected: A list of notes shown. The status bar at the bottom saysNotesand the UI looks like this: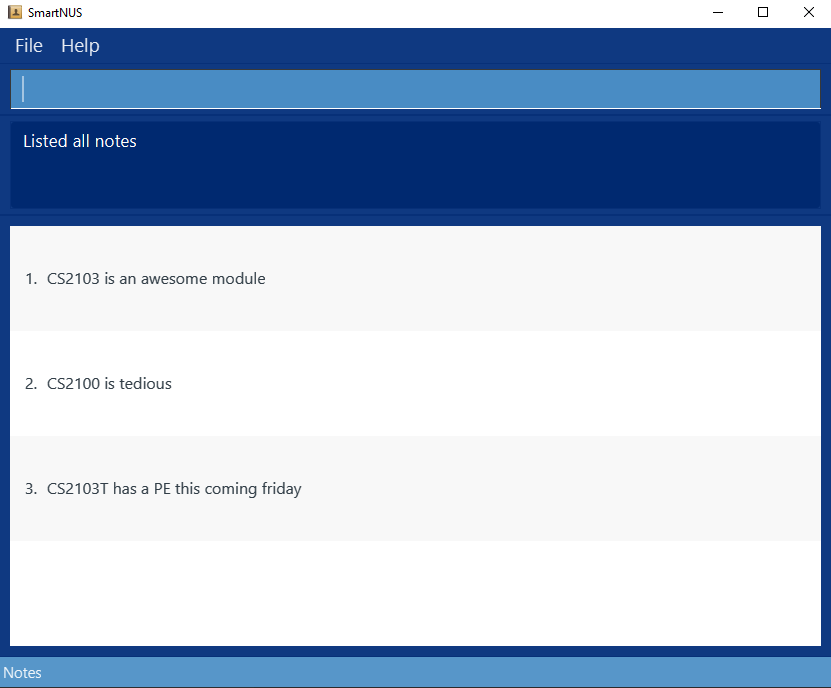
- Test case:
- Switch panel to view all tags
- Test case:
list tag
Expected: A list of tags and their statistics shown. The status bar at the bottom saysTagsand the UI looksl ike this: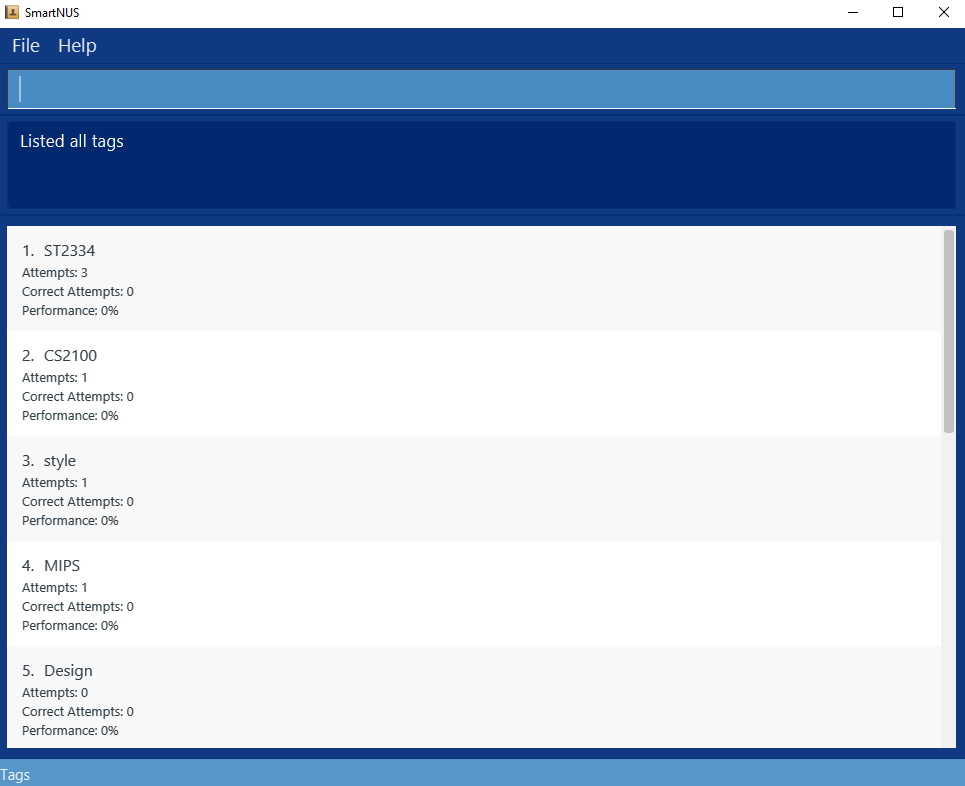
- Test case:
- Don’t switch panel
- Test case:
list abc
Expected: Stay in the current panel and an error message is shown sayingInvalid command format.
- Test case:
Changing Theme
- Change theme to light Theme
- Test case:
theme light
Expected: The color scheme of the app will have light colors. The UI will have this color scheme: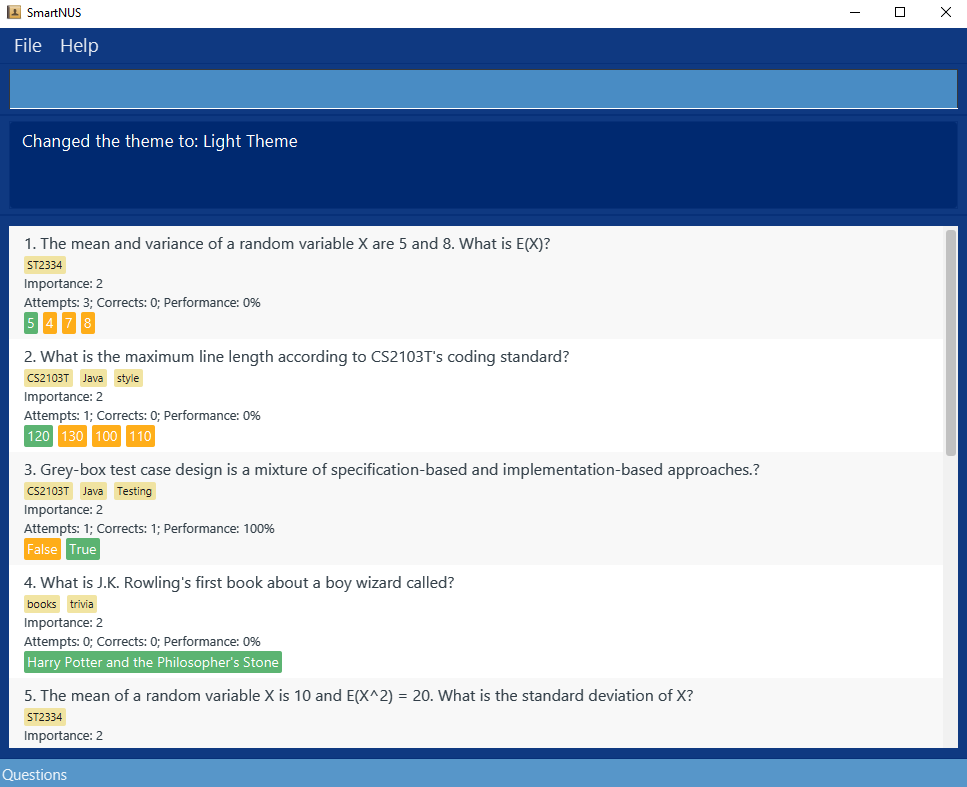
- Test case:
- Change theme to dark theme
- Test case:
theme dark
Expected: The color scheme of the app will have dark colors. The UI will have this color scheme: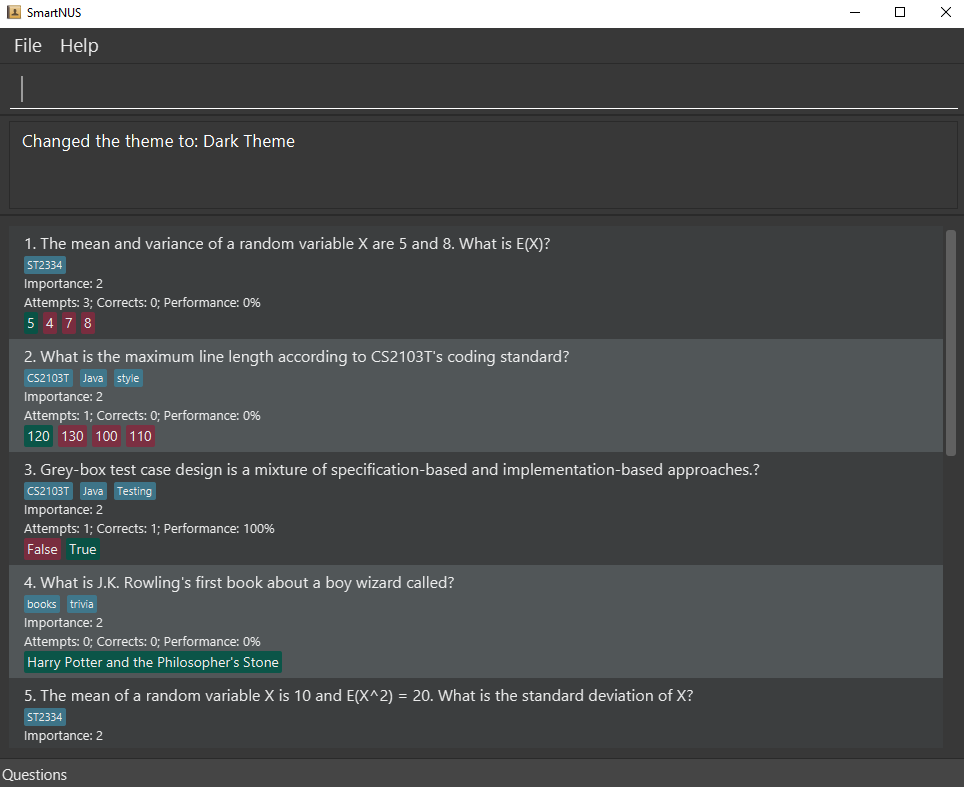
- Test case:
- Don’t change theme
- Test case:
theme not a theme
Expected: The theme will not change and an error message will be shown sayingInvalid command format.Quiz
- Test case:
-
Answering a multiple choice question
-
Prerequisites: The question being displayed is a multiple choice question.
-
Test case:
A
Expected: The question is answered with option ‘A’. Details of whether the option is correct or incorrect is displayed. -
Test case:
a
Expected: Similar to previous. -
Test case:
E
Expected: Question is not answered. Error details shown in the status message. -
Other incorrect delete commands to try:
e,asdf,ans
Expected: Similar to previous.
-
-
Answering a true false question
-
Prerequisites: The question being displayed is a true false question.
-
Test case:
True
Expected: The question is answered with option ‘True’. Details of whether the option is correct or incorrect is displayed. -
Test case:
T
Expected: Similar to previous. -
Test case:
A
Expected: Question is not answered. Error details shown in the status message. -
Other incorrect delete commands to try:
True,tru,flase
Expected: Similar to previous.
-
-
Answering a short answer question
-
Prerequisites: The question being displayed is a short answer question
-
Test case:
ans/Hello There
Expected: The question is answered with answer ‘Hello There’. Details of whether the answer is correct or incorrect is displayed. -
Test case:
Hello There
Expected: Question is not answered. Error details shown in the status message. -
Other incorrect delete commands to try:
ans/,an/Hello,ansHello There
Expected: Similar to previous.
-
-
Proceeding to the next question
-
Prerequisites: The question being displayed is not the last question.
-
Test case:
next
Expected: The next question in the quiz will be displayed. Status bar will be updated with the updated question number. -
Test case:
nxt
Expected: The question displayed remains the same. Error details shown in the status message. -
Other incorrect delete commands to try:
n,nextt,nex t
Expected: Similar to previous.
-
-
Proceeding to the previous question
-
Prerequisites: The question being displayed is not the last question.
-
Test case:
prev
Expected: The next question in the quiz will be displayed. Status bar will be updated with the updated question number. -
Test case:
pre
Expected: The question displayed remains the same. Error details shown in the status message. -
Other incorrect delete commands to try:
p,prevv,pre v
Expected: Similar to previous.
-
Quiz specific questions
-
Prerequisites: There needs to be at least 5 questions in the question list. And the user needs to be in the question panel by doing
list question. - Quiz single question
-
Test case:
quiz n/1
Expected: A quiz window will open and only 1 question will be tested, particularly the first question in the question list you saw earlier. The status bar of the quiz window should state that there is only 1 question in the quiz. -
Test case:
quiz n/100
Expected: A quiz window will not open and an error message will say thatQuiz has no questions.
-
- Quiz multiple question
-
Test case:
quiz n/1 2
Expected: A quiz window will open and 2 questions will be tested, particularly the first and second question in the question list you saw earler. Donextcommand to confirm that the second question is indeed the second question in the list. The status bar of the quiz window should state that there are 2 questions in the quiz. -
Test case:
quiz n/1 500
Expected: A quiz window will open but only 1 question will be tested, specifically the first question. Since there is no question 500, only question 1 will be tested. The status bar of the quiz window should state that there is only 1 question in the quiz.
-
Quiz with tags and limits
-
Prerequisites: use the dummy data by deleting the saved data file at
data/smartnus.json. And the user needs to be in the question panel by doinglist question. - Quiz only tags
-
Test case:
quiz t/st2334
Expected: Only 2 questions will be in the quiz. -
Test case:
quiz t/cs2103t t/java
Expected: Only 4 questions will be in the quiz. -
Test case:
quiz t/abc def
Expected: Quiz window will not open and an error message will show that theTag is invalid.
-
- Quiz limit
-
Test case:
quiz lim/3
Expected: Only 3 questions will be in the quiz. -
Test case:
quiz lim/100
Expected: Only 9 questions will be in the quiz as there are only 9 questions. -
Test case:
quiz lim/abc
Expected: Quiz window will not open and an error message will show that theLimit is invalid.
-
- Quiz limit and and tag
- Test case:
quiz lim/3 t/cs2103t
Expected: 3 Quiz with a tag of cs2103T will be shown.
- Test case:
Stat
- Prerequisites:
- List all questions using the
list questioncommand. Multiple questions in the list. - Add a few questions if there are none.
- Add tags A and B to different questions, using the edit command. e.g.
edit 1 t/A - Do a few quizzes using the
quizcommand. - List all statistics using the
list tagcommand.
- List all questions using the
-
Test case:
stat t/A
Expected: Overall statistics for questions tagged with A are shown. -
Test case:
stat t/A t/B
Expected: Overall statistics for questions tagged with A and questions tagged with B are shown. The lower performance statistic is shown first. - Other incorrect stat commands to try:
stat adfasExpected: Error message is shown as this in an invalid command format.
Adding a note
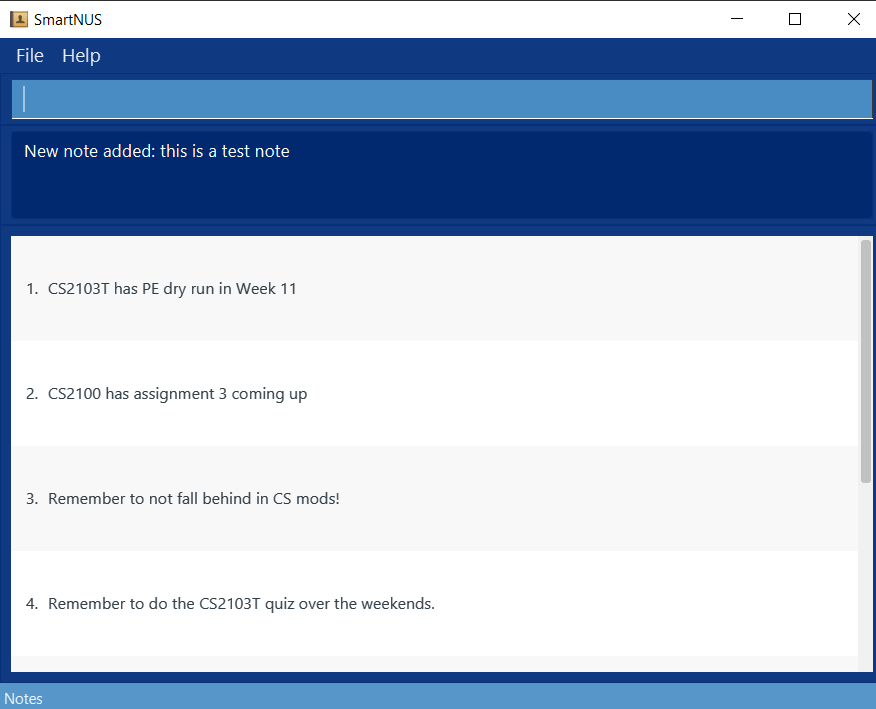
- Successfully add a note in english.
- Prerequisite: On the Note panel/viewing notes (if not, run the
list notecommand) - Test case
note note/this is a test noteExpected: A new note will be added and SmartNus will look like:
- Prerequisite: On the Note panel/viewing notes (if not, run the
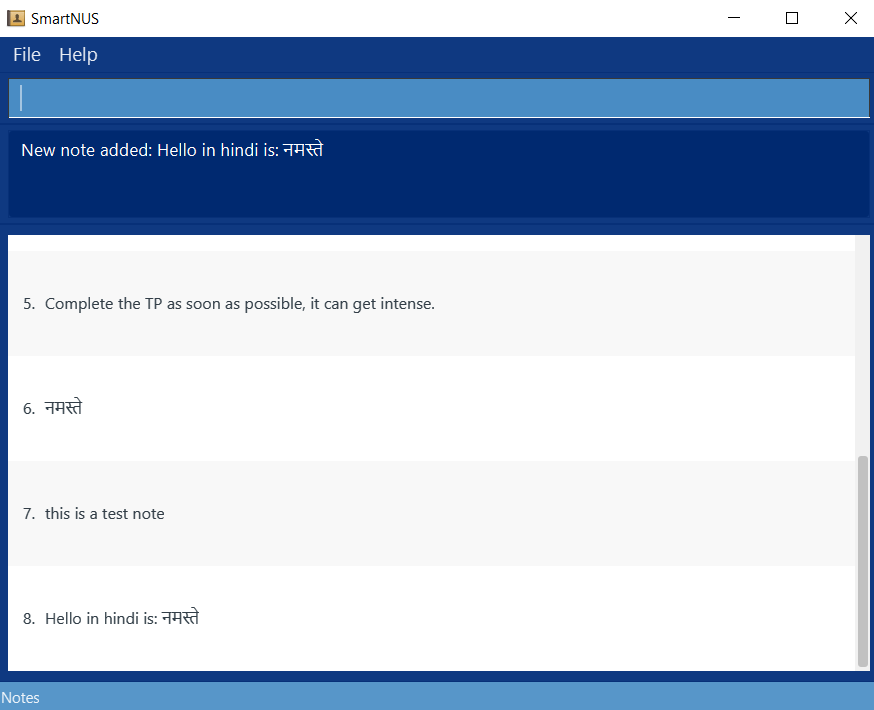
- Successfully add a note in another language
- Prerequisite: On the Note panel/viewing notes (if not, run the
list notecommand) - Test case
note note/Hello in hindi is: नमस्तेExpected: A new note will be added and SmartNus will look like:
- Prerequisite: On the Note panel/viewing notes (if not, run the
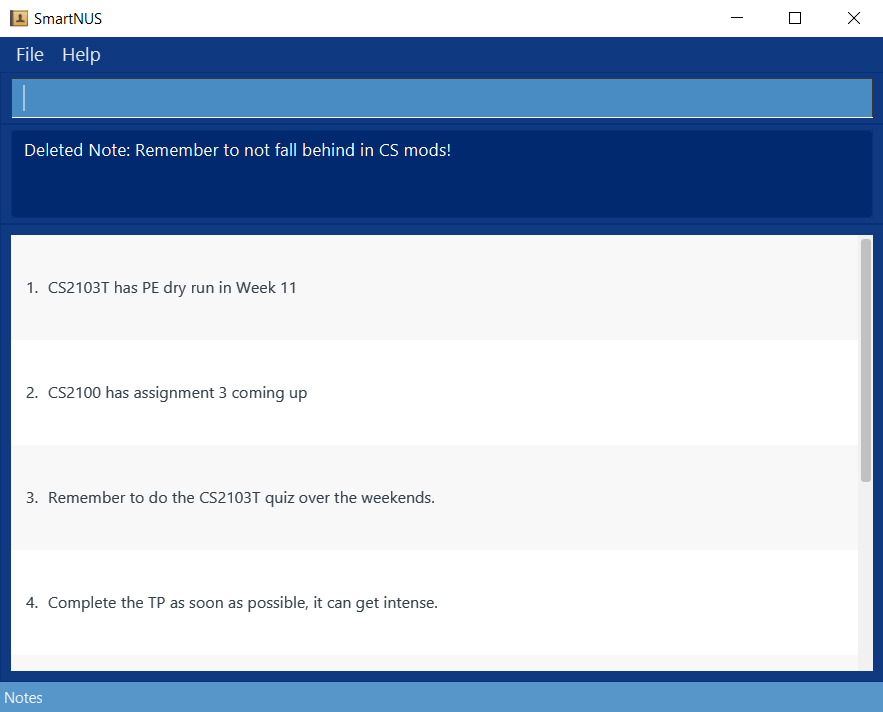
- Successfully delete a note
- Prerequisite: On the Note panel/viewing notes (if not, run the
list notecommand) and there are at least 3 notes in the note list. - Test case
delete note 3Expected: A success message comes and the 3rd note gets deleted. SmartNus looks like:
- Prerequisite: On the Note panel/viewing notes (if not, run the
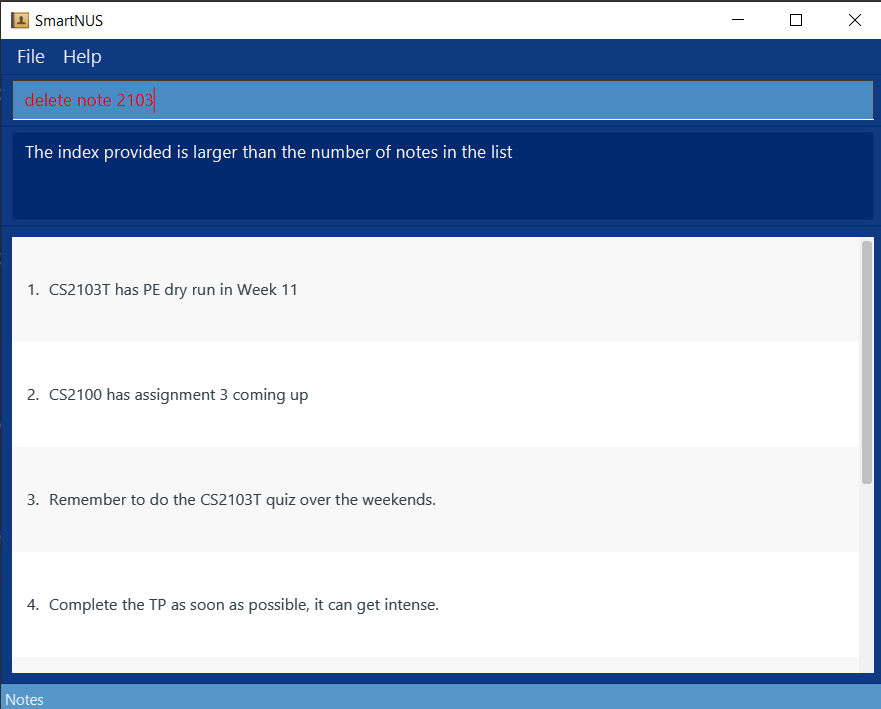
- Give an invalid index for note deletion
- Prerequisite: On the Note panel/viewing notes (if not, run the
list notecommand) and there are at least 3 notes in the note list. - Test case
delete note 2103Expected: An error message pops up and note list is unchanged. SmartNus looks like:
- Prerequisite: On the Note panel/viewing notes (if not, run the
Saving data
-
Dealing with missing/corrupted data files
-
Prerequisites: have a saved data located in
docs/smartnus.json. If you don’t have it, launch the app and it should generate dummy data for you. Close the app after that. -
Test case: Update the
importanceof the first question in the saved data (docs/smartnus.json) into a valud of"300". This will cause the saved data file to be corrupted.
Expected: When launching the app all the data will not be shown.
-